What is chlamydia?
Chlamydia is a common STD that can infect both men and women. It can cause serious, permanent damage to a woman’s reproductive system, making it difficult or impossible for her to get pregnant later on.
Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted disease (STD) that can be easily cured.
If left untreated, chlamydia can make it difficult for a woman to get pregnant
How is chlamydia spread?
- You can get chlamydia by having vaginal, anal, or oral sex with someone who has chlamydia.
- If your sex partner is male you can still get chlamydia even if he does not ejaculate (cum).
- If you’ve had chlamydia and were treated in the past, you can still get infected again if you have unprotected sex with someone who has chlamydia.
- If you are pregnant, you can give chlamydia to your baby during childbirth.
How can I reduce my risk of getting chlamydia?
- The only way to avoid STDs is to not have vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
If you are sexually active, you can do the following things to lower your chances of getting chlamydia:
- Being in a long-term mutually monogamous relationship with a partner who has been tested and has negative STD test results;
- Using latex condoms the right way every time you have sex.
Am I at risk for chlamydia?
- Anyone who has sex can get chlamydia through unprotected vaginal, anal, or oral sex. However, sexually active young people are at a higher risk of getting chlamydia. This is due to behaviors and biological factors common among young people. Gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men are also at risk since chlamydia can be spread through oral and anal sex.
- Have an honest and open talk with your health care provider and ask whether you should be tested for chlamydia or other STDs. If you are a sexually active woman younger than 25 years, or an older woman with risk factors such as new or multiple sex partners, or a sex partner who has a sexually transmitted infection, you should get a test for chlamydia every year. Gay, bisexual, and men who have sex with men; as well as pregnant women should also be tested for chlamydia.
How do I know if I have chlamydia?
Most people who have chlamydia have no symptoms. If you do have symptoms, they may not appear until several weeks after you have sex with an infected partner. Even when chlamydia causes no symptoms, it can damage your reproductive system.
Women with symptoms may notice
- An abnormal vaginal discharge;
- A burning sensation when urinating.
Symptoms in men can include
- A discharge from their penis;
- A burning sensation when urinating;
- Pain and swelling in one or both testicles (although this is less common).
Men and women can also get infected with chlamydia in their rectum, either by having receptive anal sex, or by spread from another infected site (such as the vagina).
While these infections often cause no symptoms, they can cause
- Rectal pain;
- Discharge;
- Bleeding
You should be examined by doctor if you notice any of these symptoms or if your partner has an STD or symptoms of an STD, such as an unusual sore, a smelly discharge, burning when urinating, or bleeding between periods.
Lab test for chlamydia
- There are laboratory tests to diagnose chlamydia. Your health care provider may ask you to provide a urine sample or may use (or ask you to use) a cotton swab to get a sample from your vagina to test for chlamydia.
Can chlamydia be cured?
- Yes, chlamydia can be cured with the right treatment. It is important that you take all of the medication your doctor prescribes to cure your infection. When taken properly it will stop the infection and could decrease your chances of having complications later on. Medication for chlamydia should not be shared with anyone.
- Repeat infection with chlamydia is common. You should be tested again about three months after you are treated, even if your sex partner(s) was treated.
I was treated for chlamydia. When can I have sex again?
- You should not have sex again until you and your sex partner(s) have completed treatment. If your doctor prescribes a single dose of medication, you should wait seven days after taking the medicine before having sex. If your doctor prescribes a medicine for you to take for seven days, you should wait until you have taken all of the doses before having sex.
What happens if I don’t get treated?
- The initial damage that chlamydia causes often goes unnoticed. However, chlamydia can lead to serious health problems.
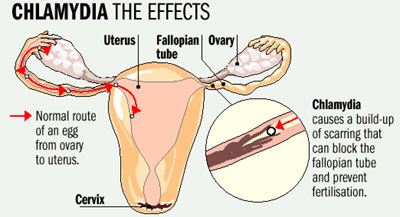
- If you are a woman, untreated chlamydia can spread to your uterus and fallopian tubes (tubes that carry fertilized eggs from the ovaries to the uterus), causing pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). PID often has no symptoms, however some women may have abdominal and pelvic pain. Even if it doesn’t cause symptoms initially, PID can cause permanent damage to your reproductive system and lead to long-term pelvic pain,inability to get pregnant, and potentially deadly ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy outside the uterus).
- Men rarely have health problems linked to chlamydia. Infection sometimes spreads to the tube that carries sperm from the testicles, causing pain and fever. Rarely, chlamydia can prevent a man from being able to have children.
Untreated chlamydia may also increase your chances of getting or giving HIV – the virus that causes AIDS.
Homeopathy treatment for Chlamydia
Symptomatic Homeopathy medicines helps for Chlamydia
For more details & Consultation Feel free to contact us.
Vivekanantha Clinic Consultation Champers at
Chennai:- 9786901830
Panruti:- 9443054168
Pondicherry:- 9865212055 (Camp)
Mail : consult.ur.dr@gmail.com, homoeokumar@gmail.com
For appointment please Call us or Mail Us
For appointment: SMS your Name -Age – Mobile Number – Problem in Single word – date and day – Place of appointment (Eg: Rajini – 30 – 99xxxxxxx0 – white discharge, yeast infection,TV, itching in vagina, watery discharge from vagina, – 21st Oct, Sunday – Chennai ), You will receive Appointment details through SMS
.